The threat of cyber attacks continues to grow at an outrageous pace. Ransomware, data breaches, phishing attacks, identity fraud, and denial-of-service attacks are all growing in terms of scale, sophistication, and capability.
This has led to an unprecedented spike in cyber insurance claims, with some reports suggesting that the number has risen by 100% over the past few years.
We wrote this article for businesses that are looking to obtain cyber insurance or expand your current policy to cover more areas of risk. It’s designed to provide all the steps you need to develop a comprehensive cyber insurance coverage checklist and to understand the strategies you can use to avoid policy exclusions and other pitfalls.
Meet the cyber insurance coverage policy requirements with Complete Network.
Learn More
A cyber insurance risk assessment is necessary to identify your company’s vulnerabilities before you can acquire cyber insurance.
This assessment should analyze not only threats to your technology, but also weaknesses in business practices, protocols, and procedures that may also pose a security danger. Such an evaluation is advantageous to both your organization and the insurer.
You’ll gain a precise and detailed view of your business and all related vulnerabilities, while the insurance company gets all the information they require to underwrite your cyber insurance policy.
A risk assessment starts by determining all your organization’s high-value assets that are most in jeopardy of attack; that means taking inventory of your laptops, mobile devices, servers, software systems, databases, and sensitive data. It also involves evaluating third-party risk from vendors and contractors.
Tips to remember when evaluating risks include:
When it comes to emergency preparedness, the best time to put your incident response and business continuity plans to the test is before the emergency arises.
This is the only way to ensure that your planning is comprehensive and will meet the needs of your organization in the event of a real-world crisis.
There is a significant overlap between incident response and business continuity planning, but they are fundamentally distinct processes that address different problems.
An incident response plan (IRP) is activated in the immediate aftermath of a crisis to contain and mitigate the incident. Think of the IRP as largely focused on the technical aspects of the situation, such as identifying and eradicating malware.
A business continuity plan (BCP), on the other hand, is designed to keep critical business functions running throughout the lifecycle of an emergency. The BCP takes a more holistic approach that’s focused on keeping core business operations up and running despite the seriously debilitating interruption at hand.
While cyber risks like data breaches, ransomware attacks, and system downtime are the chief concerns of decision-makers today, a valid IRP and BCP must also prepare the organization for other wide-scale interruptions, such as a natural disaster, power outage, fire, flood, or any other event that could impact day-to-day operations.
Developing these plans may seem like a daunting task, but there are many resources available, such as working with a trusted managed services provider to help get your strategies in order.
By preparing today, you can minimize the impact of an incident tomorrow and keep your business operations running smoothly, no matter what obstacles you might face.
A Verizon report published in 2022 found that the vast majority of cyberattacks can be attributed to employee error.
Whether it’s misconfigured databases and servers, easy-to-guess passwords, or clicking phishing links, these missteps open the door for cybercriminals to enter and cause mayhem on an organization’s systems.
As a result, compliance and cybersecurity awareness training has become an essential feature of the modern companies’ security regimen.
In fact, depending on the industry you serve, your company could be legally obligated to deliver compliance and awareness training based on specific cyber security and data privacy frameworks, with notable examples being HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and FISMA.
A good compliance and security awareness program must be constructed based on knowledge, appreciation, and behavior:
Here are 10 items you’ll want to incorporate into your training program to satisfy insurers:
Considering that your in-house IT team is already inundated with support tickets and requests, providing comprehensive network security training to your workforce can be a challenge.
For those organizations looking to create a culture of security through awareness training programs, a dependable managed services provider can offer the necessary support and resources needed to reach proficiency and avoid business interruption.
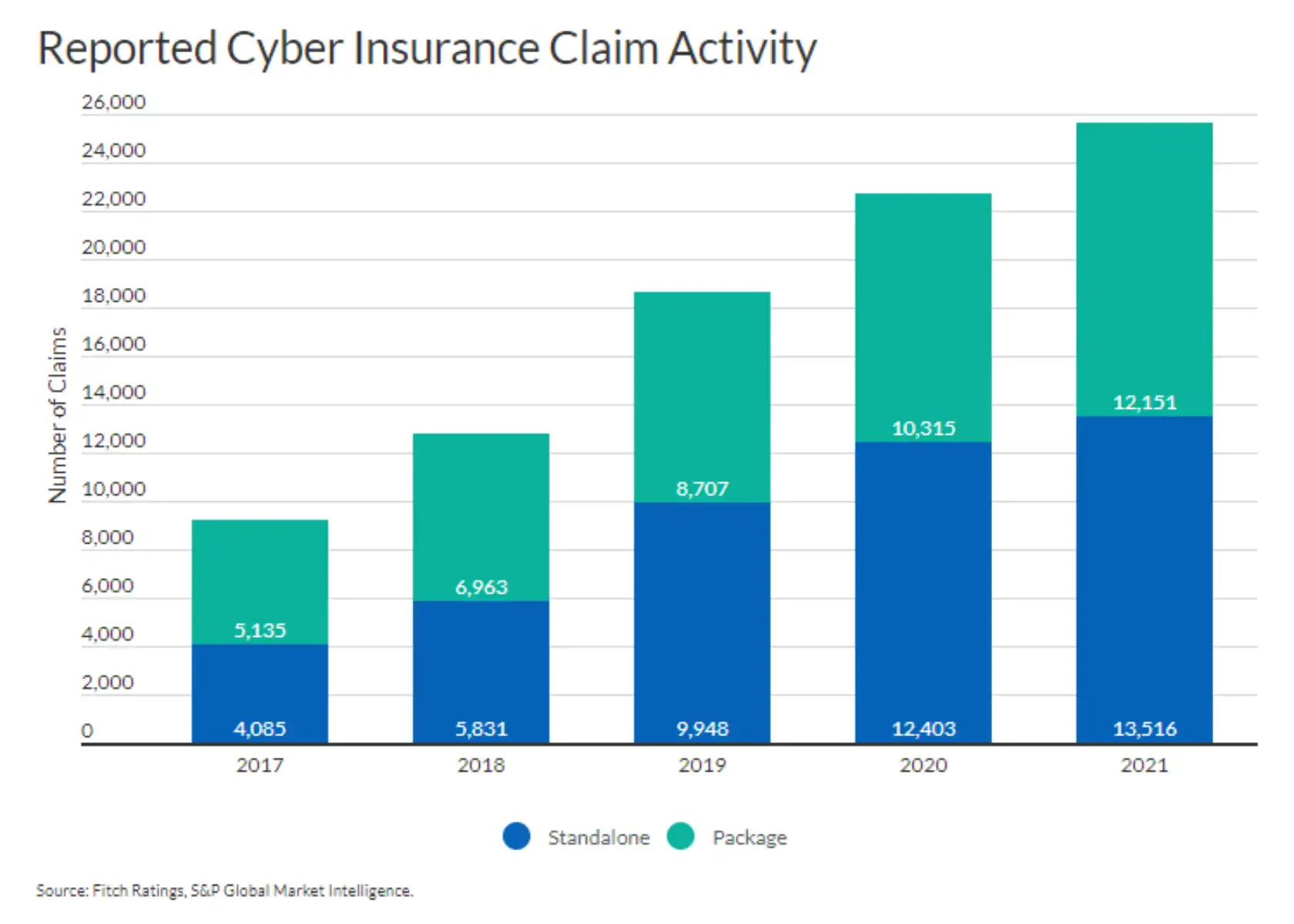
Source: Fitch Ratings
Clearly defining your company’s cyber insurance coverage policy requirements is the next step in crafting your cyber security insurance coverage checklist.
There are many different types of cyber liability insurance coverage available under a cyber insurance policy. Your job is to draw from the discoveries uncovered during the previous steps to make an informed decision that will cover any gaps in your preparedness and response efforts.
Broadly speaking, the different types of cyber insurance can be divided into two main groups: first-party insurance and third-party insurance.
First-party coverage is designed to protect policyholders against attacks targeting their networks and business systems. Typically, this type of policy will pay out an indemnity for cyber incidents such as:
Third-party insurance covers the policyholder from claims levied against them made by other parties.
For example, if a person files a lawsuit alleging that they’ve become the victim of identity theft after hackers infiltrate your network, third-party coverage will minimize your financial liabilities.
Third-party cyber insurance will usually cover the cost of the following:
The final point to keep in mind when creating your cyber insurance coverage checklist is that all policies aren’t created equal. Therefore, it’s important that you’re aware of the common pitfalls and exclusions that may leave your company with insufficient cybersecurity insurance coverage.
Often, cyber insurance policies will have exclusions for the following:
Going a step further, to get the most out of your cyber insurance policy, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the various triggers that can activate coverage. Here are some examples of common cyber insurance triggers:
Of course, every policy is different and has its own specific coverage terms and triggers. It’s always best to review your policy and consult with your insurer when there’s a need for clarification carefully and routinely.
In addition, your IT team should have a comprehensive understanding of your coverage and the triggers therein.
| Interested in learning more about cyber security? Check out these blogs: |
Cyber insurance is an important purchase for any business. Taking the time to create a cyber insurance coverage checklist will ensure that you’re well-prepared and have the right types of coverage in place.
Clarifying requirements and purchasing insurance with the help of an experienced cybersecurity partner make the whole process even easier.
If you need help navigating the purchase of a cyber insurance policy, contact us today to schedule a consultation with our cybersecurity experts. We’re here to help!
In an ideal world, technology would be a consistent source of competitive advantage and benefit for small and midsized businesses. The reality is that many fail to realize that confidence.
Without the right resources and support, even a highly skilled technology team can become overwhelmed by the growing list of technology management duties. When important tasks get neglected, it creates ripple effects throughout an organization that damage productivity and efficiency.
The co-managed IT services model solves these problems by providing your existing IT team with all the support and resources they need to successfully plan, manage, and defend your network technology.
This guide covers:
This will close in 0 seconds
This will close in 0 seconds