An incident management plan is crucial for ensuring your business can recover quickly and minimize losses during a crisis. Yet, 77% of organizations lack such a plan, which leaves them at risk if an incident occurs. Usually, the reason for this gap is simply an unfamiliarity with the correct incident response steps.
“A successful incident response can prevent a minor issue from turning into a major organizational crisis.” – Jeremy Wanamaker, CEO of Complete Network.
Your incident response process will be somewhat unique to your business. The types of threats you face, the size of your organization, and the resources available will all influence your approach.
However, there are specific best practices that every organization should follow. These steps will both reduce the impact of security incidents and reduce the likelihood of future incidents. Our article will explore these essential steps so you can keep your systems secure.
The NIST incident response lifecycle is a widely recognized incident response framework that many organizations use as their frame of reference when they develop their own plan. This framework was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and is separated into 4 key phases of incident response.
| Phase | Activities Involved |
| 1. Preparation |
|
| 2. Detection and Analysis |
|
| 3. Containment, Eradication, and Recovery |
|
| 4. Post-Incident Activity |
|
To break down the 4 phases further, we have created a 10-step plan that you can use to help yourself develop your organization’s incident response framework.
Ensure every department clearly understands its role during an incident to reduce confusion and enhance coordination. Each team should know how their responsibilities contribute to resolving the issue quickly. This alignment enables smoother collaboration and faster recovery when time is critical.
Predefine the communication methods used during incidents to share information quickly and accurately. These channels should be reliable and accessible across the entire organization. Consistent communication helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures all teams stay updated as the situation evolves.
Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities your organization may face. Develop policies that define how to address these threats and gather the necessary tools you may need to deal with them. Train employees on these procedures and regularly update their knowledge to reflect new threats or technologies.
Continuous system monitoring helps detect potential threats early, which is crucial because a persistent threat can stay undetected in a network for an average of 51 days. Implement an incident logging system to document unusual behaviors to enable a quicker analysis of potential risks. Train staff on interpreting data from these tools to ensure quick and accurate threat assessments when alerts occur.
Once a threat is identified, isolate the affected systems immediately to stop the spread to other parts of the network. Fast containment limits the scope of the damage and ensures that the issue does not disrupt the entire infrastructure. This could include disconnecting affected devices or shutting down specific servers to prevent further spread.
| Learn ore About How You Can Secure Your Business Operations |
Develop thorough checklists and procedures for investigating the root cause of incidents. This may involve scanning affected systems, checking for malware, or addressing software vulnerabilities. After identifying the cause, ensure that the entire threat is removed by conducting follow-up scans and testing systems for any remaining issues before declaring the threat fully eradicated.
After the incident is fully resolved, restore systems to full functionality and verify that no vulnerabilities remain. Prioritize restoring the most critical systems first to minimize operational impact. After recovery, conduct tests to ensure no residual issues remain and that systems function as expected.
Assign incident response team roles and responsibilities that outline who is responsible for each task during response efforts. Who performs which role may vary depending on who in your organization is qualified for the position. The following chart shows what roles are generally involved and who answers to who during the incident management lifecycle.
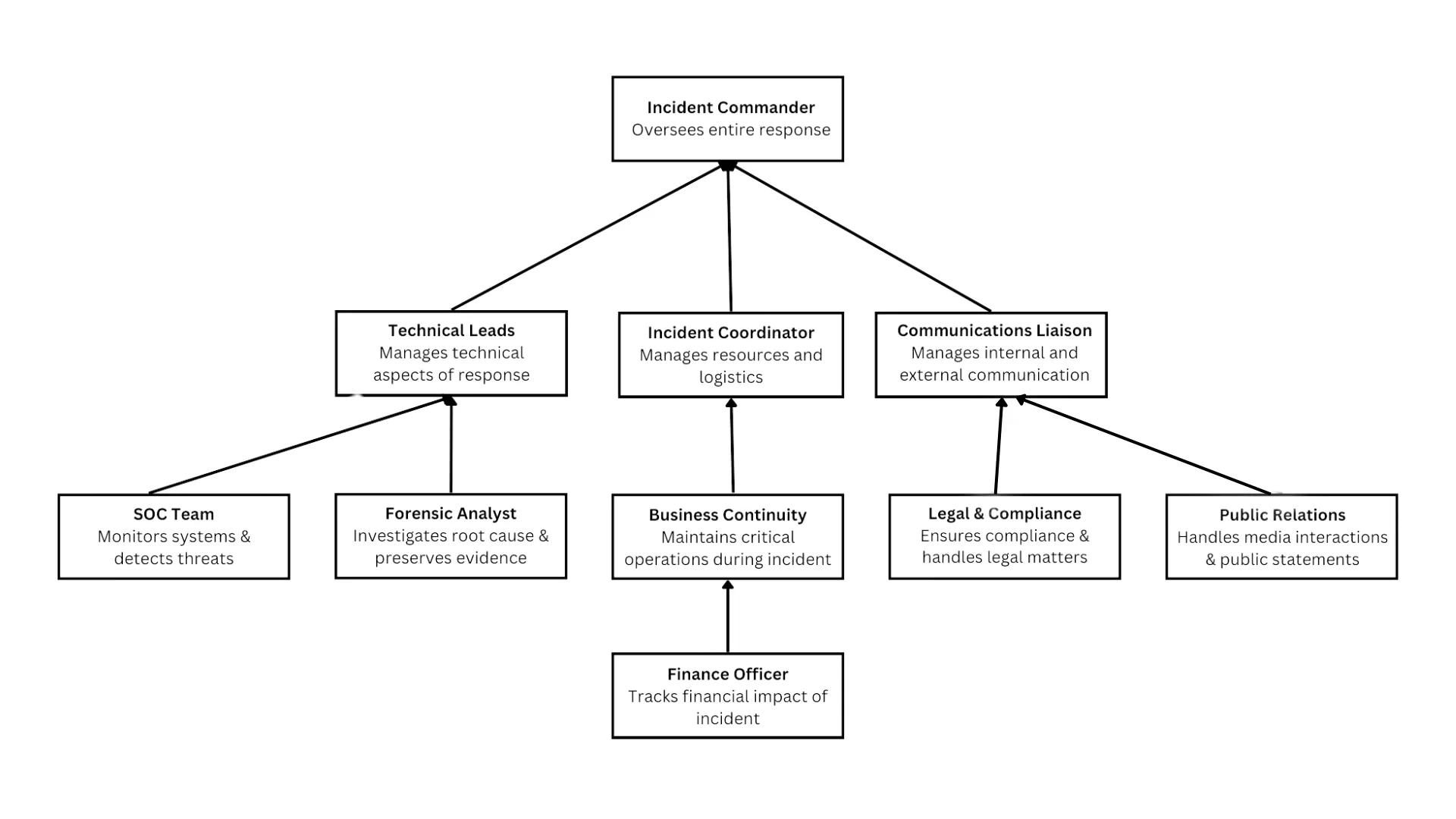
Conduct regular training sessions and simulations for all types of incidents, including data loss from accidental deletion, fire, or system failures. CloudSecureTech reports that 70% of businesses have experienced data loss due to such incidents. Simulations keep teams ready to act decisively in real-world scenarios.
Consistently review and update the incident response plan to address new threats and changes in technology. Keeping the plan up-to-date ensures that it remains effective and that your organization is prepared to handle emerging risks. Frequent updates improve readiness and reduce the chances of being caught off-guard by new vulnerabilities.
| Work With Incident Response Specialists in The Following Areas | ||
| Albany, NY | Charlotte, NC | Savannah, GA |
Even if you see the value of having an incident response plan and coordinated team, you may not have the time or resources to create a response framework or respond in kind. If that’s the case, you may want to consider outsourcing your incident response team.
Complete Network has experts who can help. We understand industry-leading best practices and are happy to share our insights with our clients. We’ll provide both the tools and personnel that you need for a swift incident response that minimizes potential damage.
Contact us today to learn more.
In an ideal world, technology would be a consistent source of competitive advantage and benefit for small and midsized businesses. The reality is that many fail to realize that confidence.
Without the right resources and support, even a highly skilled technology team can become overwhelmed by the growing list of technology management duties. When important tasks get neglected, it creates ripple effects throughout an organization that damage productivity and efficiency.
The co-managed IT services model solves these problems by providing your existing IT team with all the support and resources they need to successfully plan, manage, and defend your network technology.
This guide covers:
This will close in 0 seconds
This will close in 0 seconds