In a world where sensitive information is constantly exchanged online, the significance of protecting this data cannot be overstated.
Imagine a scenario where your personal details, like bank information or private messages, fall into the wrong hands.
Research shows that the first quarter of 2023 saw over 6 million data records being exposed worldwide through data breaches.
This scenario isn’t just unsettling; it’s a real threat in our increasingly connected world.
This alarming possibility highlights the critical need for robust security measures, particularly encryption.
As Jeremy Wanamaker, CEO of Complete Network, says, “Encryption is a key defender in our digital age, turning vulnerable data into inaccessible secrets, safeguarding our most sensitive information.”
In this blog, we’ll delve into the meaning of encryption, its types, and important encryption benefits to understand why it is necessary in the 21st century.
Encryption is a method of securing digital information, ensuring that sensitive data remains confidential and protected. It involves the conversion of data into a code, known as encrypted data, to prevent unauthorized access.
The process uses encryption algorithms, which are complex formulas, to transform readable data into a coded format. This coded data can only be accessed or decrypted by someone who has the appropriate encryption key, which serves as a digital codebreaker.
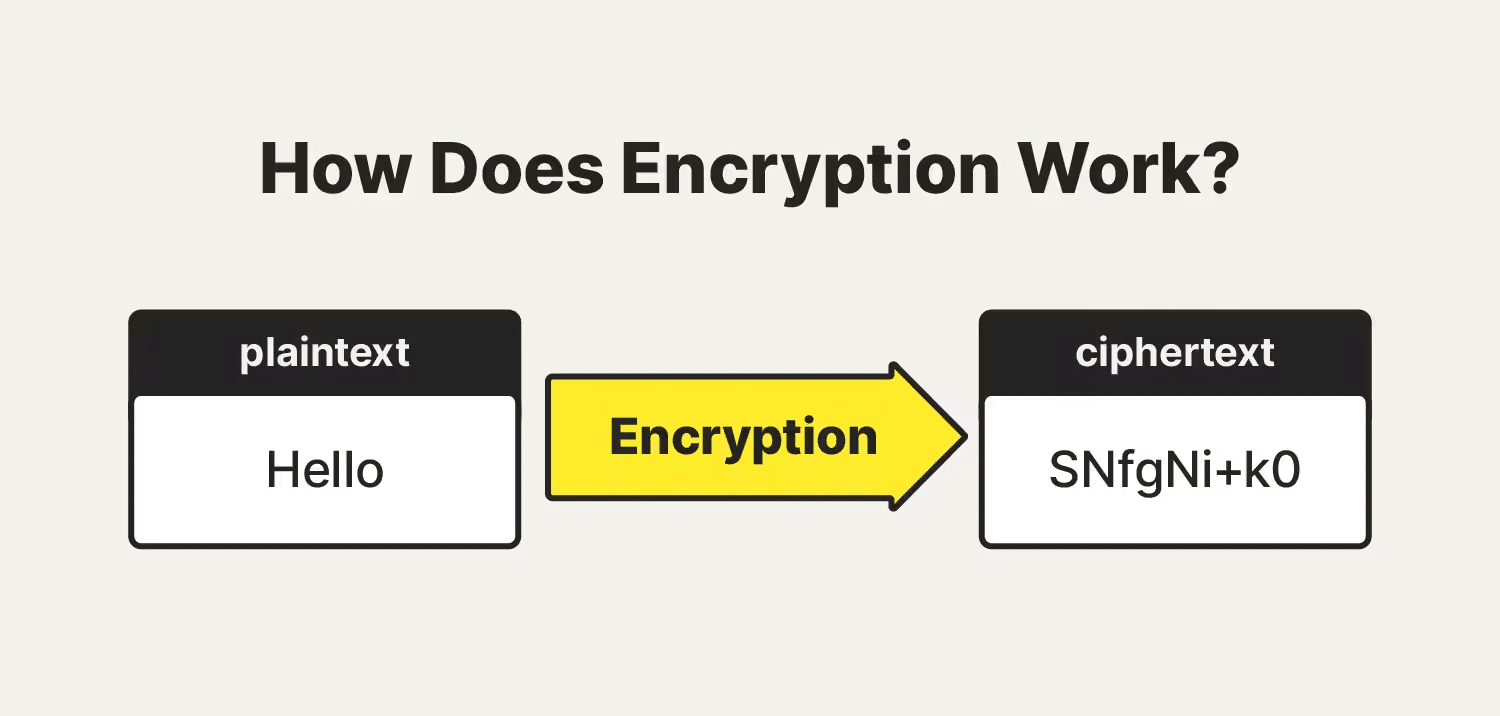
Source: Norton
There are different types of encryption, such as symmetric encryption, where the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the data, or asymmetric encryption, which uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
This technology is not just limited to safeguarding confidential business or government information; it extends to personal devices like smartphones. The benefits of encrypting phone data are significant. It ensures that personal information, such as text messages, emails, and photos, remains secure, especially if the phone is lost or stolen.
Let Complete Network’s 24/7/365 support and seasoned expertise be your shield against cyber threats.
Know More
The primary purpose of encryption is to protect the confidentiality of digital data stored on computer systems or transmitted via the Internet or other computer networks.
Encryption, while crucial for protecting sensitive information, presents a balance of significant advantages and inherent challenges. Understanding these aspects is key to effectively utilizing encryption in various contexts. Let’s take a look at both the advantages and disadvantages of data encryption.
Encryption benefits are vast and varied, but they all converge on one point: enhanced security.
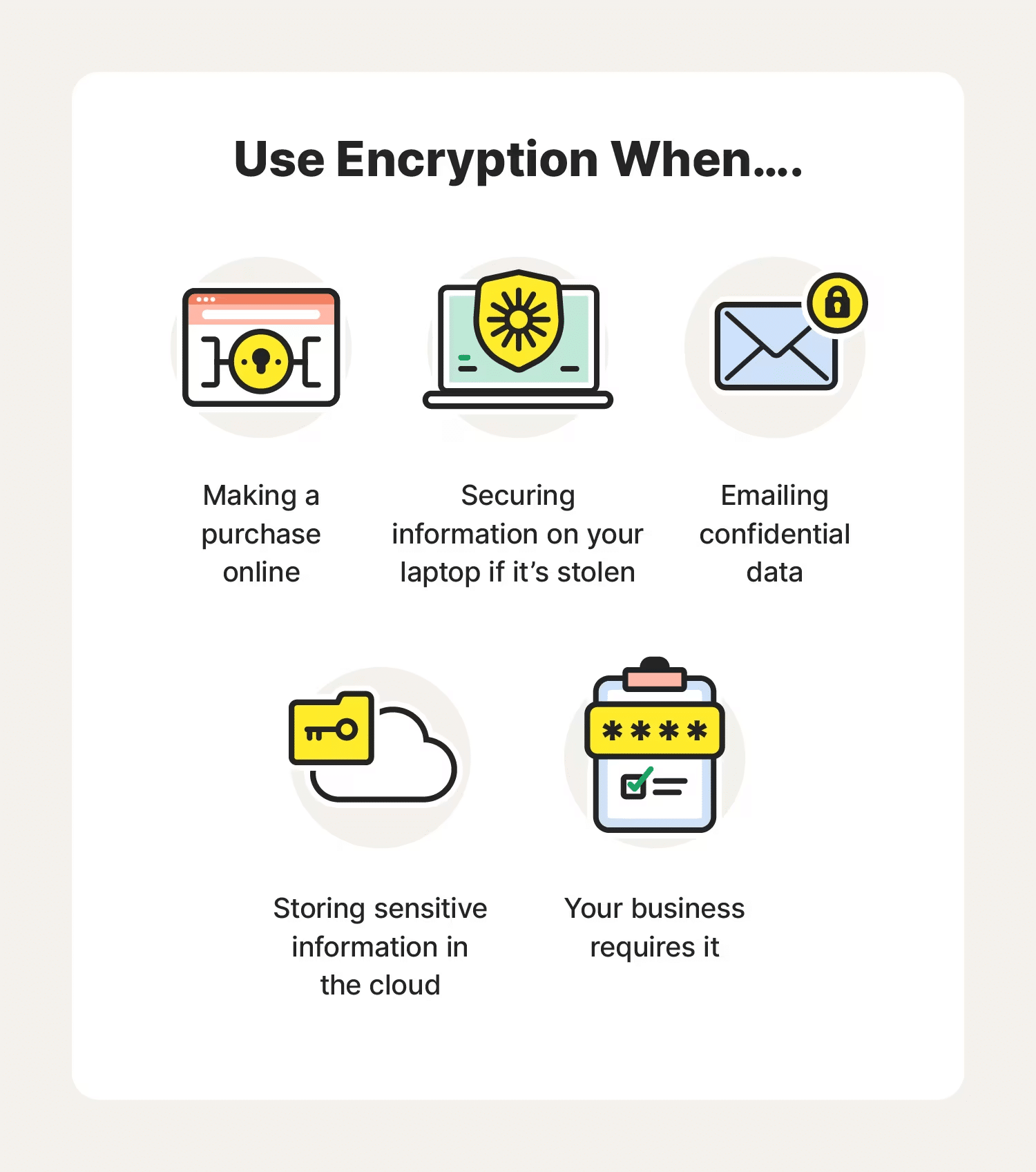
Source: Norton
Though encryption is instrumental in safeguarding data, it also brings with it certain challenges and limitations that must be carefully considered in its application.
| More resources you might like: |
| Feature | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
| Key Type | Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. | Uses a pair of keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. |
| Speed | Generally faster due to simpler algorithms. | Slower due to more complex algorithms. |
| Security | Key distribution can be challenging; if the key is compromised, data can be easily decrypted. | More secure as it does not require sharing of private keys; even if the public key is known, data remains secure. |
| Use Case | Often used for encrypting large volumes of data, e.g., database encryption. | Commonly used for secure data transmission, e.g., in emails and digital signatures. |
| Complexity | Less complex, easier to implement. | More complex, requires robust key management. |
| Examples | Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES). | RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). |
Research suggests that just by using robust encryption and enforcing cybersecurity tactics, businesses can save, on average $1.4 million for each attack.
The role of encryption in enhancing data security is undeniable and critical. It stands as a vital line of defense, protecting personal and professional data from a wide range of cyber threats.
Are you looking to enhance the cyber security of your business and wondering how encryption can fit into your overall strategy?
Contact us for expert guidance and solutions tailored to fortify your security posture with encryption.
In an ideal world, technology would be a consistent source of competitive advantage and benefit for small and midsized businesses. The reality is that many fail to realize that confidence.
Without the right resources and support, even a highly skilled technology team can become overwhelmed by the growing list of technology management duties. When important tasks get neglected, it creates ripple effects throughout an organization that damage productivity and efficiency.
The co-managed IT services model solves these problems by providing your existing IT team with all the support and resources they need to successfully plan, manage, and defend your network technology.
This guide covers:
This will close in 0 seconds
This will close in 0 seconds